Staff Nurse Recruitment Exam MCQs 1
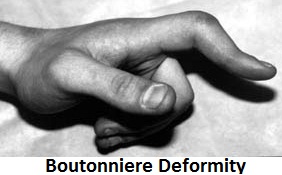
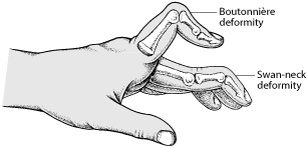
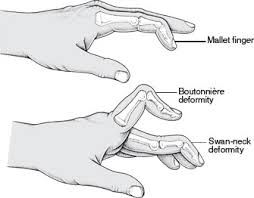
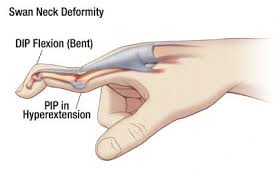
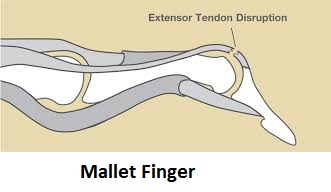
1. When the middle slip of the extensor tendon is cut there is
- No deformity
- Swan-neck deformity
- Botton-hole deformity
- Mallet finger deformity
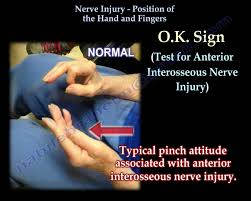
2. In anterior interosseous nerve injury there is
- Defective pinch
- Sensory loss over lateral 3 and a half fingers
- Abduction of thmb is weak
- Clawing of the lateral fingers
3. Plaster of Paris is :
- Calcium carbonate
- Calcium phosphate
- Calcium sulphate
- Calcium citrate
4. The commonest complaint of women fitted with an intrauterine device is
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pain
- Pelvic infection
- Uterine perforation
5, An example for second generation Intrauterine device is
- Lippes loop
- T-Cu-380A
- Progestasert
- Levonorgestrel
http://birthcontrol-contraceptives.blogspot.in/p/intra-uterine-devicesiud.html
https://www.drugs.com/mmx/progestasert.html
6. Salt intake as per Dietary Goals should be reduced to an average of not more than
- 5 grams per day
- 10 grams per day
- 15 grams per day
- 20 grams per day
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs393/en/
7. Prevention of Food Adulteration Act was enacted by the Indian Parliament in the year :
- 1954
- 1977
- 1985
- 1997
8. The risk of stomach cancer has been related to the deficiency of :
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Cobalt
- Nickel
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4200652/
9. Chikungunya fever is transmitted by the mosquito species :
- Aedes
- Culex
- Mansonia
- Anopheles
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs327/en/
10. About 60-80% of all reported cases of foodborne diseases are due to
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Salmonella
- Clostridium perfringens
- Bacellus cereus
11. Rickettsial pox is transmitted by the insect vector
- Louse
- Flea
- Tick
- Mite
12. Average incubation period of rubella is
- 10 days
- 14 days
- 18 days
- 21 days
13. Immunity following measles vaccination develops after ____ days:
- 2 days
- 4 days
- 8 days
- 12 days
http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p4209.pdf
14. How many types of vaccines are there against Japanese Encephalitis?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p4209.pdf
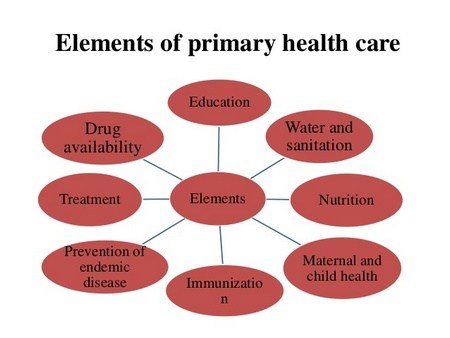
13. All of the following are elements of primary health care EXCEPT :
- Immuniztion against major infectious diseases
- Provision of essential drugs
- Prevention and control of locally endemic diseases
- Camps for periodic health checkup
14. At village level, primary health care is provided by all, EXCEPT :
- ASHA
- Anganawadi worker
- Local dais
- Multipurpose worker (Male Health Worker)
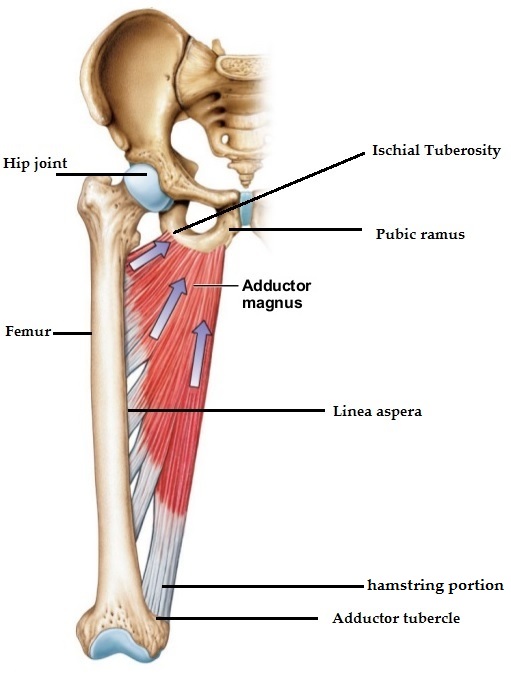
15. Hamstring muscles are :
- Tensor fascia lata, Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus
- Semitendinosus, semimembranosus, Biceps femoris, Adductor magnus
- Biceps femoris, Adductor magnus, Gracilis, Semitendinosus
- Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, Gracilis, Adductor magnus
16. Which of the following is NOT a fcharacteristic of upper motor neurone lesion :
- Muscle atrophy
- Spasticity
- Hyperreflexia
- Babinski's sign
17. In radial tunnel syndrome, the nerve entrapped is :
- Anterior interosseous neve
- Posterior interosseous nerve
- Axillary Nerve
- Radial nerve
18. Which of the following drug has the highest toxicity to a child?
- Salbutamol
- Paracetamol
- Oral contraceptives
- Tricyclic antidepressants
19. A complete loss of language comprehesion or production is called:
- Dysfluency
- Aphasia
- Dyspraxia
- Dysphasia
20. Compulsive eating of substance other than food is called
- Pica
- Polyphagia
- Ritolicha
- Anorexia
- Excess of vitamin K in a new born causes which of the following complication
- Bleeding tendencies
- Hyperbilirubinemia
- Vomiting
- Haemolysi
* * * * * * * * * *